安装 lighttpd 於 FreeBSD
作者:zeissoctopus
以下是我安装和配置 lighttpd 1.4.29 万维网服务器於 FreeBSD 8-Stable 的笔记。我会启动以下几项功能:
SSL
lighttpd 的 simple namebase virtualhost
FastCGI 支援 PHP
1: 安装软件
从 ports 编译安装 lighttpd 入 FreeBSD
% cd /usr/ports/www/lighttpd
% su root
# make install
# make clean
# exit
以下是我用 ports 编译 lighttpd 时所选择的选项
WITHOUT_BZIP2 true
WITHOUT_CML true
WITHOUT_FAM true
WITHOUT_GDBM true
WITH_IPV6 true
WITHOUT_LIBEV true
WITHOUT_MAGNET true
WITHOUT_MEMCACHE true
WITHOUT_MYSQL true
WITHOUT_MYSQLAUTH true
WITHOUT_NODELAY true
WITHOUT_OPENLDAP true
WITH_OPENSSL true
WITHOUT_SPAWNFCGI true
WITHOUT_VALGRIND true
WITHOUT_WEBDAV true
FreeBSD 默认 Httpd 使用者身份是 www:www
2: 安排网站的文件目录
lighttpd 执行时,会产生一些文件。lighttpd 也会找寻网站实际放置的位置。因此需要事先安排妥当。因为我只需要 lighttpd 为一个 domain 服务,所以我只需要依 从 simple virtualhost 规则建立网站的目录结构。然而所有文件位置皆可以自由安排,本例子是依从我个人喜好来决定而已。
lighttpd 执行时产生的文件
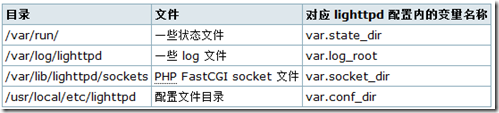
lighttpd 的 simple namebase virtualhost 目录安排
除了根目录外,其余皆以 virtual host 网站名称来命名目录

3: 配置 FreeBSD ports 里的 lighttpd
在 FreeBSD 里默认配置文件的位置

有关本例子载入配置文件的次序
本例子会启动 Lighttpd 的 ssl、fastcgi 和 simple_vhost 模块,因此有关配置文件会按以 下次序读入:
/usr/local/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
/usr/local/etc/lighttpd/modules.conf
/usr/local/etc/lighttpd/conf.d/fastcgi.conf
/usr/local/etc/lighttpd/conf.d/simple_vhost.conf
换言之,本例子只需要适当修改以上4个配置文件。
lighttpd.conf 内容
#######################################################################
##
## /usr/local/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## 定义有些有关目录的变量
##
var.log_root = "/var/log/lighttpd"
var.state_dir = "/var/run"
var.home_dir = "/var/spool/lighttpd"
var.conf_dir = "/usr/local/etc/lighttpd"
##
## Virutal Hosts 的根目录
##
## 用于以下模块:
## conf.d/evhost.conf
## conf.d/simple_vhost.conf
## vhosts.d/vhosts.template
##
var.vhosts_dir = "/home/www"
##
## CGI/FastCGI socket 目录
##
## 用于以下模块:
## conf.d/fastcgi.conf
## conf.d/scgi.conf
##
var.socket_dir = "/var/lib/lighttpd/sockets"
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## 载入模块定义文件
include "modules.conf"
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## Lighttpd 基本设定
## ———————
##
server.port = 80
## 用否 IPv6?
server.use-ipv6 = "disable"
## 缚紧 IP
server.bind = "127.0.0.1"
## Lighttpd 以什么身份执行.
server.username = "www"
server.groupname = "www"
## Server: 回应字串
server.tag = "lighttpd"
## Lighttpd 的 pid 文件
server.pid-file = state_dir + "/lighttpd.pid"
## 默认文件目录
server.document-root = "/home/www/example.org/htdocs/"
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## Logging 选项
## ——————
##
server.errorlog = log_root + "/lighttpd-error.log"
##
## Access log config
##
include "conf.d/access_log.conf"
##
## The debug options are moved into their own file.
## see conf.d/debug.conf for various options for request debugging.
##
include "conf.d/debug.conf"
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## Tuning/Performance
## ——————–
##
server.event-handler = "freebsd-kqueue"
##
## The basic network interface for all platforms at the syscalls read()
## and write(). Every modern OS provides its own syscall to help network
## servers transfer files as fast as possible
##
## linux-sendfile – is recommended for small files.
## writev – is recommended for sending many large files
##
server.network-backend = "writev"
##
## As lighttpd is a single-threaded server, its main resource limit is
## the number of file descriptors, which is set to 1024 by default (on
## most systems).
##
## If you are running a high-traffic site you might want to increase this
## limit by setting server.max-fds.
##
## Changing this setting requires root permissions on startup. see
## server.username/server.groupname.
##
## By default lighttpd would not change the operation system default.
## But setting it to 2048 is a better default for busy servers.
##
server.max-fds = 2048
##
## Stat() call caching.
##
## lighttpd can utilize FAM/Gamin to cache stat call.
##
## possible values are:
## disable, simple or fam.
##
server.stat-cache-engine = "simple"
##
## Fine tuning for the request handling
##
## max-connections == max-fds/2 (maybe /3)
## means the other file handles are used for fastcgi/files
##
server.max-connections = 1024
##
## How many seconds to keep a keep-alive connection open,
## until we consider it idle.
##
## Default: 5
##
server.max-keep-alive-idle = 5
##
## How many keep-alive requests until closing the connection.
##
## Default: 16
##
server.max-keep-alive-requests = 16
##
## Maximum size of a request in kilobytes.
## By default it is unlimited (0).
##
## Uploads to your server cant be larger than this value.
##
server.max-request-size = 0
##
## Time to read from a socket before we consider it idle.
##
## Default: 60
##
server.max-read-idle = 60
##
## Time to write to a socket before we consider it idle.
##
## Default: 360
##
server.max-write-idle = 360
##
## Traffic Shaping
## —————–
##
## see /usr/share/doc/lighttpd/traffic-shaping.txt
##
## Values are in kilobyte per second.
##
## Keep in mind that a limit below 32kB/s might actually limit the
## traffic to 32kB/s. This is caused by the size of the TCP send
## buffer.
##
## per server:
##
server.kbytes-per-second = 128
##
## per connection:
##
connection.kbytes-per-second = 32
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## Filename/File handling
## ————————
##
## files to check for if …/ is requested
## index-file.names = ( "index.php", "index.rb", "index.html",
## "index.htm", "default.htm" )
##
index-file.names += (
"index.xhtml", "index.html", "index.htm", "index.php"
)
##
## deny access the file-extensions
##
## ~ is for backupfiles from vi, emacs, joe, …
## .inc is often used for code includes which should in general not be part
## of the document-root
url.access-deny = ( "~", ".inc" )
##
## disable range requests for pdf files
## workaround for a bug in the Acrobat Reader plugin.
##
$HTTP["url"] =~ "\.pdf$" {
server.range-requests = "disable"
}
##
## which extensions should not be handle via static-file transfer
##
## .php, .pl, .fcgi are most often handled by mod_fastcgi or mod_cgi
##
static-file.exclude-extensions = ( ".php", ".php5", ".pl", ".fcgi", ".scgi" )
##
## mimetype mapping
##
include "conf.d/mime.conf"
##
## directory listing configuration
##
include "conf.d/dirlisting.conf"
##
## Should lighttpd follow symlinks?
##
server.follow-symlink = "disable"
##
## force all filenames to be lowercase?
##
server.force-lowercase-filenames = "disable"
##
## defaults to /var/tmp as we assume it is a local harddisk
##
server.upload-dirs = ( "/var/tmp" )
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## SSL Settings
##
$SERVER["socket"] == ":443" {
ssl.engine = "enable"
ssl.pemfile = "/usr/local/etc/ssl/crt/YourHost.pem"
ssl.use-sslv3 = "enable"
ssl.cipher-list = "TLSv1+HIGH:SSLv3+HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!3DES:@STRENGTH"
}
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## Simple virtual host
##
$HTTP["host"] != "wiki.example.org" {
accesslog.filename = log_root + "/example.org-access.log"
}
$HTTP["host"] == "wiki.example.org" {
accesslog.filename = log_root + "/wiki.example.org-access.log"
}
modules.conf 内容
#######################################################################
##
## Modules to load
## —————–
##
## at least mod_access and mod_accesslog should be loaded
## all other module should only be loaded if really neccesary
##
## – saves some time
## – saves memory
##
## the default module set contains:
##
## "mod_indexfile", "mod_dirlisting", "mod_staticfile"
##
## you dont have to include those modules in your list
##
## Modules, which are pulled in via conf.d/*.conf
##
## NOTE: the order of modules is important.
##
## – mod_accesslog -> conf.d/access_log.conf
## – mod_compress -> conf.d/compress.conf
## – mod_status -> conf.d/status.conf
## – mod_webdav -> conf.d/webdav.conf
## – mod_cml -> conf.d/cml.conf
## – mod_evhost -> conf.d/evhost.conf
## – mod_simple_vhost -> conf.d/simple_vhost.conf
## – mod_mysql_vhost -> conf.d/mysql_vhost.conf
## – mod_trigger_b4_dl -> conf.d/trigger_b4_dl.conf
## – mod_userdir -> conf.d/userdir.conf
## – mod_rrdtool -> conf.d/rrdtool.conf
## – mod_ssi -> conf.d/ssi.conf
## – mod_cgi -> conf.d/cgi.conf
## – mod_scgi -> conf.d/scgi.conf
## – mod_fastcgi -> conf.d/fastcgi.conf
## – mod_proxy -> conf.d/proxy.conf
## – mod_secdownload -> conf.d/secdownload.conf
## – mod_expire -> conf.d/expire.conf
##
server.modules = (
"mod_access",
"mod_alias",
"mod_auth",
# "mod_evasive",
"mod_redirect",
"mod_rewrite",
"mod_setenv",
# "mod_usertrack",
)
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## Config for various Modules
##
##
## mod_ssi
##
#include "conf.d/ssi.conf"
##
## mod_status
##
#include "conf.d/status.conf"
##
## mod_webdav
##
#include "conf.d/webdav.conf"
##
## mod_compress
##
#include "conf.d/compress.conf"
##
## mod_userdir
##
#include "conf.d/userdir.conf"
##
## mod_magnet
##
#include "conf.d/magnet.conf"
##
## mod_cml
##
#include "conf.d/cml.conf"
##
## mod_rrdtool
##
#include "conf.d/rrdtool.conf"
##
## mod_proxy
##
#include "conf.d/proxy.conf"
##
## mod_expire
##
#include "conf.d/expire.conf"
##
## mod_secdownload
##
#include "conf.d/secdownload.conf"
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## CGI modules
##
##
## SCGI (mod_scgi)
##
#include "conf.d/scgi.conf"
##
## FastCGI (mod_fastcgi)
##
include "conf.d/fastcgi.conf"
##
## plain old CGI (mod_cgi)
##
#include "conf.d/cgi.conf"
##
#######################################################################
#######################################################################
##
## VHost Modules
##
## Only load ONE of them!
## ========================
##
##
## You can use conditionals for vhosts aswell.
##
## see http://www.lighttpd.net/documentation/configuration.html
##
##
## mod_evhost
##
#include "conf.d/evhost.conf"
##
## mod_simple_vhost
##
include "conf.d/simple_vhost.conf"
##
## mod_mysql_vhost
##
#include "conf.d/mysql_vhost.conf"
##
#######################################################################
fastcgi.conf 内容
以下 fastcgi.conf 仅支援 PHP5,并以 socket 方式来连接 Lighttpd 和 FastCGI Daemon,在 FreeBSD 里,php-cgi 是放在 /usr/local/bin 目录。
#######################################################################
##
## FastCGI Module
## —————
##
## http://www.lighttpd.net/documentation/fastcgi.html
##
server.modules += ( "mod_fastcgi" )
##
## PHP Example
## For PHP don’t forget to set cgi.fix_pathinfo = 1 in the php.ini.
##
## The number of php processes you will get can be easily calculated:
##
## num-procs = max-procs * ( 1 + PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN )
##
## for the php-num-procs example it means you will get 17*5 = 85 php
## processes. you always should need this high number for your very
## busy sites. And if you have a lot of RAM. 🙂
##
fastcgi.server = ( ".php" =>
( "php-local" =>
(
"socket" => socket_dir + "/php-fcgi.socket",
"bin-path" => "/usr/local/bin/php-cgi",
"bin-environment" => (
"PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN" => "8",
"PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS" => "10000",
),
"max-procs" => 1,
"broken-scriptfilename" => "enable",
)
),
)
simple_vhost.conf 内容
simple_vhost.conf
#######################################################################
##
## Simple Virtual hosting
## ————————
##
## http://www.lighttpd.net/documentation/simple-vhost.html
##
server.modules += ( "mod_simple_vhost" )
## If you want name-based virtual hosting add the next three settings and load
## mod_simple_vhost
##
## document-root =
## virtual-server-root + virtual-server-default-host + virtual-server-docroot
## or
## virtual-server-root + http-host + virtual-server-docroot
##
simple-vhost.server-root = vhosts_dir + "/"
simple-vhost.default-host = "example.org"
simple-vhost.document-root = "htdocs"
##
## Print some errors for finding the document-root
##
#simple-vhost.debug = "enable"
##
#######################################################################
4: 启动 Lighttpd 服务
请在 /etc/rc.conf 加入以下一行。那么每次重启 FreeBSD 皆会自动启动 Lighttpd
lighttpd_enable="YES"
不想重启 FreeBSB,立即启动 Lighttpd 的话,按上面修改 /etc/rc.conf 后输入以下命令便可。
% su –
# service lighttpd start
# exit
原文链接:http://wiki.freebsdchina.org/doc/l/lighttpd_1_14_29